

#7 – Controllable CostĬontrollable costs are ones where a manager (or board) decides what will happen at a particular cost. If you have invested money in a business that has gone bankrupt, it is a sunk cost already (even though you may recuperate some of the revenue through the court system). They are excluded from future business decisions. They cannot be recovered regardless of what happens. Sunk costs are costs that will not be recovered by the business. If you are deciding to rent vs buy a new piece of equipment, then you could compute the opportunity cost with all of the variables. What has to be understood is that there is always a potentially superior investment, and you need to shoot for ‘good’ as opposed to perfect. The opportunity cost is the cost associated when you go with one investment, and potentially lose out on other investments. This is usually only relevant when deciding between more than one potential business opportunity. They are essential for business operations but are not involved in the manufacturing process directly or indirectly. Rent and utilities are typical examples of operating costs. Operating costs are costs that are associated with daily business activity but are distinct from indirect costs. These are sometimes referred to as operating expenses.

Even if you pay more for components and if you pay more for hours worked, this still goes under direct costs in most instances. But remember that a variable cost is not a direct cost. The more products you produce, the more you will pay for packaging and distribution. In direct contrast to a fixed cost, a variable cost can change depending on business performance. Fixed costs are easier to calculate as they tend to be more tangible. Regardless of how well or poorly the business is doing, a fixed cost will always remain a fixed cost. A fixed interest rate repayment on a loan is also a fixed cost (provided it is not tied to a variable interest rate).
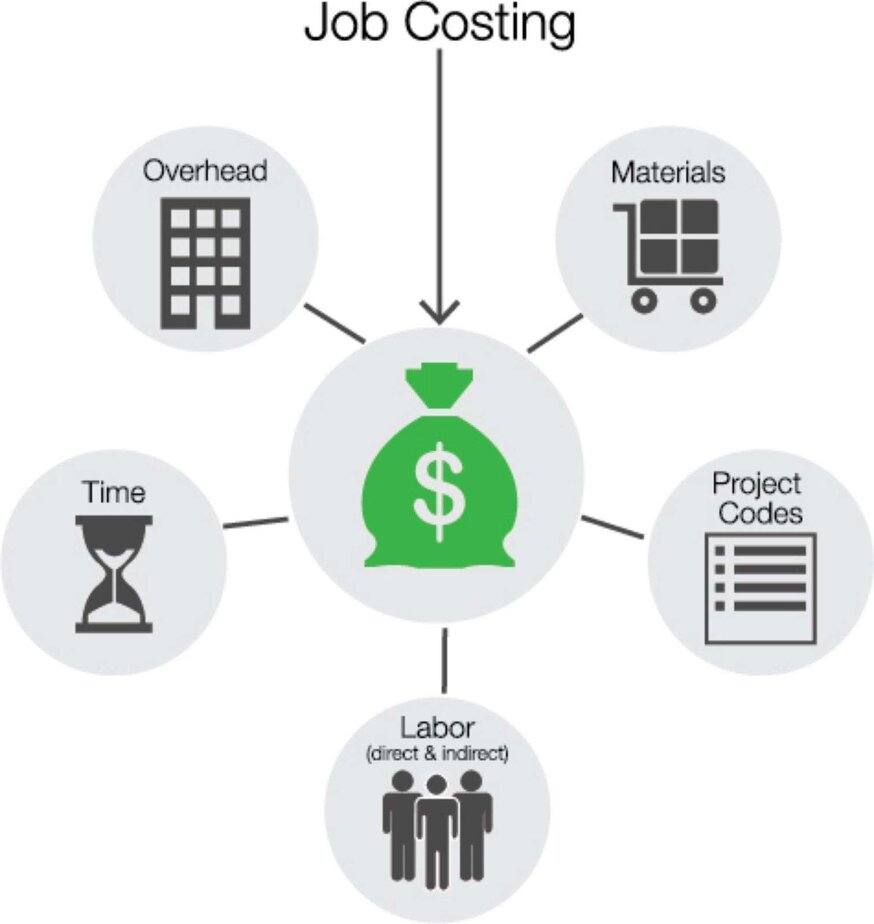
The defining characteristic of a fixed cost is that it does not change. If you need to pay $3,000 a month for the next 2 years for a property, then this is a fixed cost. The most obvious example of a fixed cost would be a lease. The direct costs would be the total cost of the individual parts themselves. The most obvious example of a direct cost would be a car manufacturing company. They may also include distribution costs and other expenses, depending on the method of accounting. Direct costs would include labor or materials. They are the direct cost associated with the production of a product.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
